react 源码-scheduler & lane
Scheduler
Scheduler主要的功能是时间切片和调度优先级
时间切片
在浏览器的一帧中 js 的执行时间如下

requestIdleCallback是在浏览器重绘重排之后,如果还有空闲就可以执行的时机,所以为了不影响重绘重排,可以在浏览器在requestIdleCallback中执行耗性能的计算,但是由于requestIdleCallback存在兼容和触发时机不稳定的问题,scheduler中采用MessageChannel来实现requestIdleCallback,当前环境不支持MessageChannel就采用setTimeout。
在之前的介绍中我们知道在performUnitOfWork之后会执行render阶段和commit阶段,如果在浏览器的一帧中,cpu 的计算还没完成,就会让出 js 执行权给浏览器,这个判断在workLoopConcurrent函数中,shouldYield就是用来判断剩余的时间有没有用尽。在源码中每个时间片时5ms,这个值会根据设备的fps调整。
1 | function workLoopConcurrent() { |
1 | function forceFrameRate(fps) { |
任务的暂停
在shouldYield函数中有一段,所以可以知道,如果当前时间大于任务开始的时间 + yieldInterval,就打断了任务的进行。
1 | //deadline = currentTime + yieldInterval,deadline是在performWorkUntilDeadline函数中计算出来的 |
调度优先级
在 Scheduler 中有两个函数可以创建具有优先级的任务
runWithPriority
以一个优先级执行 callback,如果是同步的任务,优先级就是 ImmediateSchedulerPriority
1 | function unstable_runWithPriority(priorityLevel, eventHandler) { |
scheduleCallback
以一个优先级注册 callback,在适当的时机执行,因为涉及过期时间的计算,所以 scheduleCallback 比 runWithPriority 的粒度更细。
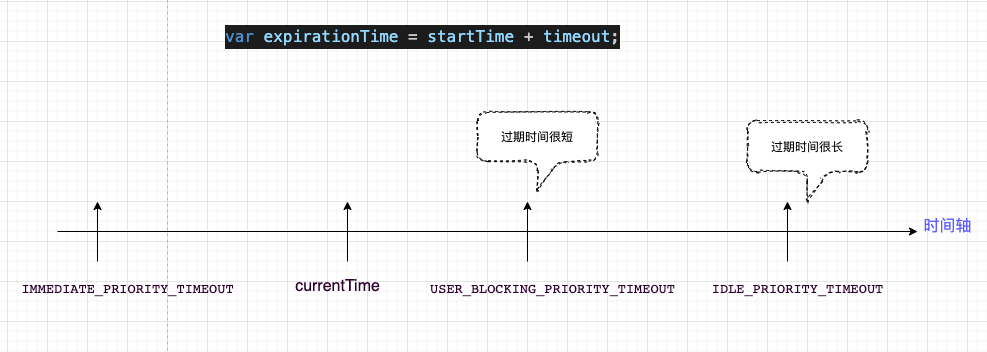
在 scheduleCallback 中优先级意味着过期时间,优先级越高 priorityLevel 就越小,过期时间离当前时间就越近,var expirationTime = startTime + timeout;例如 IMMEDIATE_PRIORITY_TIMEOUT=-1,那 var expirationTime = startTime + (-1);就小于当前时间了,所以要立即执行。
scheduleCallback 调度的过程用到了小顶堆,所以我们可以在 O(1)的复杂度找到优先级最高的 task,不了解可以查阅资料,在源码中小顶堆存放着任务,每次 peek 都能取到离过期时间最近的 task。
scheduleCallback 中,未过期任务 task 存放在 timerQueue 中,过期任务存放在 taskQueue 中。
新建 newTask 任务之后,判断 newTask 是否过期,没过期就加入 timerQueue 中,如果此时 taskQueue 中还没有过期任务,timerQueue 中离过期时间最近的 task 正好是 newTask,则设置个定时器,到了过期时间就加入 taskQueue 中。
当 timerQueue 中有任务,就取出最早过期的任务执行。
1 | function unstable_scheduleCallback(priorityLevel, callback, options) { |
任务暂停之后怎么继续
在workLoop函数中有这样一段
1 | const continuationCallback = callback(didUserCallbackTimeout); //callback就是调度的callback |
在performConcurrentWorkOnRoot函数的结尾有这样一个判断,如果callbackNode等于originalCallbackNode那就恢复任务的执行
1 | if (root.callbackNode === originalCallbackNode) { |
Lane
Lane的和Scheduler是两套优先级机制,相比来说Lane的优先级粒度更细,Lane的意思是车道,类似赛车一样,在task获取优先级时,总是会优先抢内圈的赛道,Lane表示的优先级有一下几个特点。
可以表示不同批次的优先级
从代码中中可以看到,每个优先级都是个31位二进制数字,1表示该位置可以用,0代表这个位置不能用,从第一个优先级
NoLanes到OffscreenLane优先级是降低的,优先级越低1的个数也就越多(赛车比赛外圈的车越多),也就是说含多个1的优先级就是同一个批次。1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30export const NoLanes: Lanes = /* */ 0b0000000000000000000000000000000;
export const NoLane: Lane = /* */ 0b0000000000000000000000000000000;
export const SyncLane: Lane = /* */ 0b0000000000000000000000000000001;
export const SyncBatchedLane: Lane = /* */ 0b0000000000000000000000000000010;
export const InputDiscreteHydrationLane: Lane = /* */ 0b0000000000000000000000000000100;
const InputDiscreteLanes: Lanes = /* */ 0b0000000000000000000000000011000;
const InputContinuousHydrationLane: Lane = /* */ 0b0000000000000000000000000100000;
const InputContinuousLanes: Lanes = /* */ 0b0000000000000000000000011000000;
export const DefaultHydrationLane: Lane = /* */ 0b0000000000000000000000100000000;
export const DefaultLanes: Lanes = /* */ 0b0000000000000000000111000000000;
const TransitionHydrationLane: Lane = /* */ 0b0000000000000000001000000000000;
const TransitionLanes: Lanes = /* */ 0b0000000001111111110000000000000;
const RetryLanes: Lanes = /* */ 0b0000011110000000000000000000000;
export const SomeRetryLane: Lanes = /* */ 0b0000010000000000000000000000000;
export const SelectiveHydrationLane: Lane = /* */ 0b0000100000000000000000000000000;
const NonIdleLanes = /* */ 0b0000111111111111111111111111111;
export const IdleHydrationLane: Lane = /* */ 0b0001000000000000000000000000000;
const IdleLanes: Lanes = /* */ 0b0110000000000000000000000000000;
export const OffscreenLane: Lane = /* */ 0b1000000000000000000000000000000;优先级的计算的性能高
例如,可以通过二进制按位与来判断
a和b代表的lane是否存在交集1
2
3export function includesSomeLane(a: Lanes | Lane, b: Lanes | Lane) {
return (a & b) !== NoLanes;
}
Lane 模型中 task 时怎么获取优先级的(赛车的初始赛道)
任务获取赛道的方式是从高优先级的lanes开始的,这个过程发生在 findUpdateLane 函数中,如果高优先级没有可用的 lane 了就下降到优先级低的lanes中寻找,其中 pickArbitraryLane 会调用 getHighestPriorityLane 获取一批lanes中优先级最高的那一位,也就是通过lanes & -lanes获取最右边的一位
1 | export function findUpdateLane( |
Lane 模型中高优先级时怎么插队的(赛车抢赛道)
在Lane模型中如果一个低优先级的任务执行,并且还在调度的时候触发了一个高优先级的任务,则高优先级的任务打断低优先级任务,此时应该先取消低优先级的任务,因为此时低优先级的任务可能已经进行了一段时间,Fiber树已经构建了一部分,所以需要将Fiber树还原,这个过程发生在函数prepareFreshStack中,在这个函数中会初始化已经构建的Fiber树
1 | function ensureRootIsScheduled(root: FiberRoot, currentTime: number) { |
1 | function prepareFreshStack(root: FiberRoot, lanes: Lanes) { |
Lane 模型中怎么解决饥饿问题(最后一名赛车最后也要到达终点啊)
在调度优先级的过程中,会调用 markStarvedLanesAsExpired 遍历 pendingLanes(未执行的任务包含的 lane),如果没过期时间就计算一个过期时间,如果过期了就加入 root.expiredLanes 中,然后在下次调用 getNextLane 函数的时候会优先返回 expiredLanes
1 | export function markStarvedLanesAsExpired( |
1 | export function getNextLanes(root: FiberRoot, wipLanes: Lanes): Lanes { |
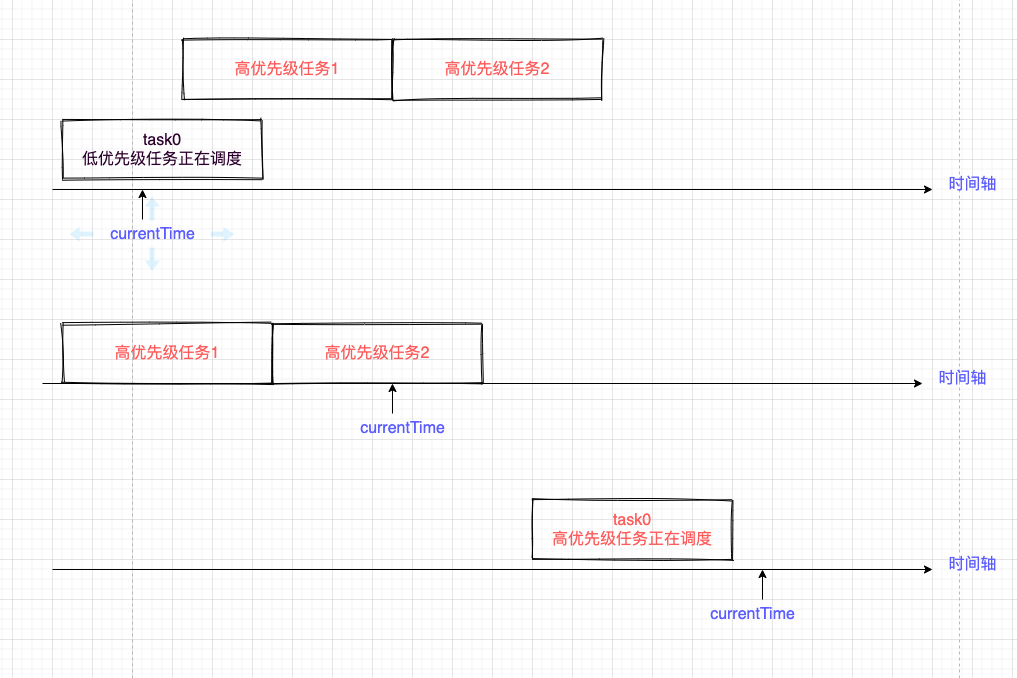
下图更直观,随之时间的推移,低优先级的任务被插队,最后也会变成高优先级的任务